Charger Soshine T2



This is a usb powered universal charger.




The charger comes in a cardboard box with specifications on the back. The display showed on the box do not match the display on the charger!

The pack contained the charger, a power supply cable and a instruction sheet.

The charger has a usb power input that can be used with the supplied usb power supply or any other usb power supply.



The supplied usb charger has a 1.5A rating.

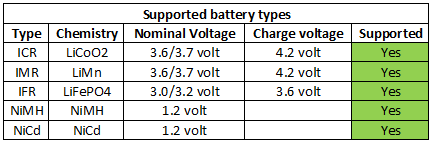
The user interface is a display and two buttons, one for each slot. The buttons is used to turn on the backlights, select display and select chemistry (Done without a battery in the slots).

Here is all elements on the display.
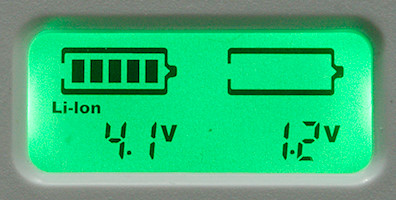
The charger is missing a NiMH text, but supports them anyway.

Charged capacity display.
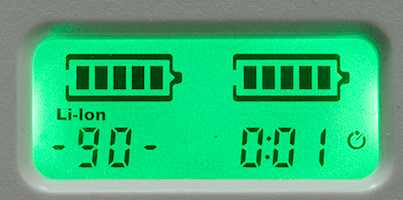
Charge percent and timer display.

The charger is rated to use up to 2A.


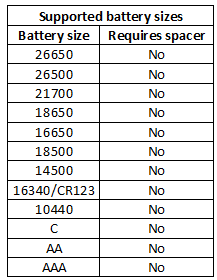
The charger uses the usual slider construction, they slide smoothly. The can be used with batteries from 31mm to 71mm










Measurements on charger
-
LiIon batteries will be discharged with 5mA when power is off.
-
NiMH batteries will be discharged with 1.5mA when power is off.
-
LiIon batteries will be discharged with 5mA when charging stops.
-
Charger will silent recharge batteries when voltage drops below 4.12V
-
Voltmeter is within 0.1V
-
Below 0.6V the charger will not see a battery
-
Below 2.2V the charger assumes NiMH
-
Above 2.2V the charger assumes LiIon.
-
Power consumption when idle is 0.25 watt from mains with supplied power supply.
Charging 4.2V LiIon
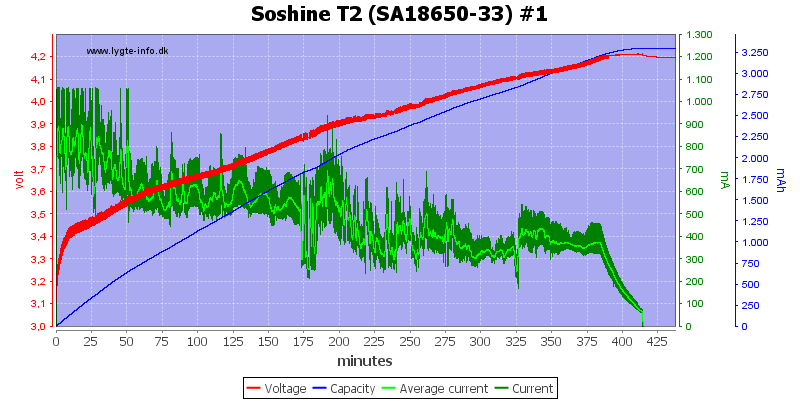
I do not really know what to call this charge curve, it do finish with a CV phase and terminates at about 100mA, this means the battery is charged fine enough.
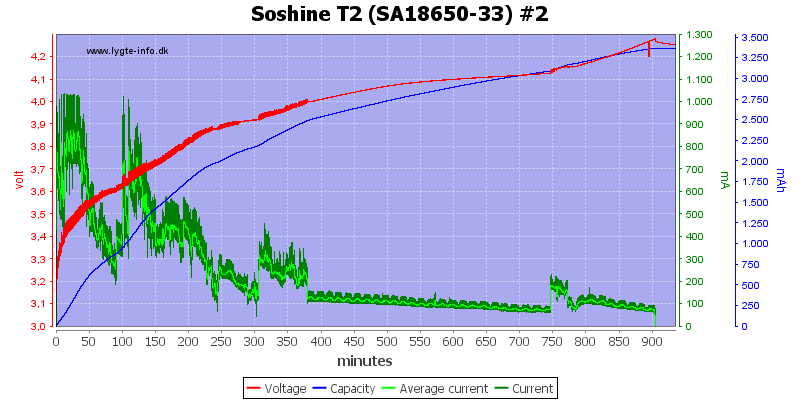
On this channel the final voltage is a bit high.
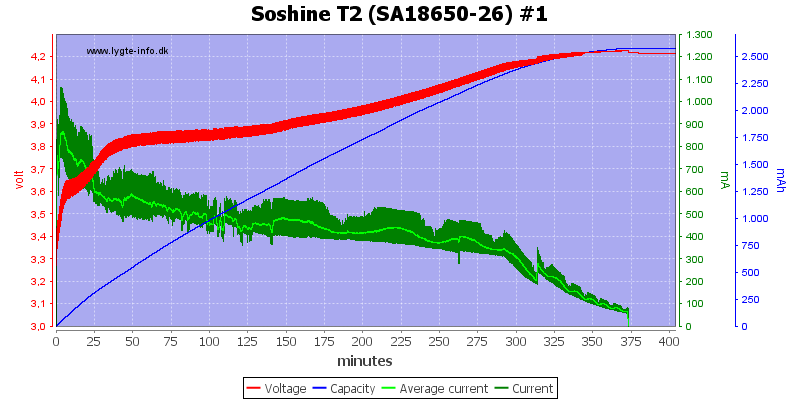

The batteries are charged fine enough.
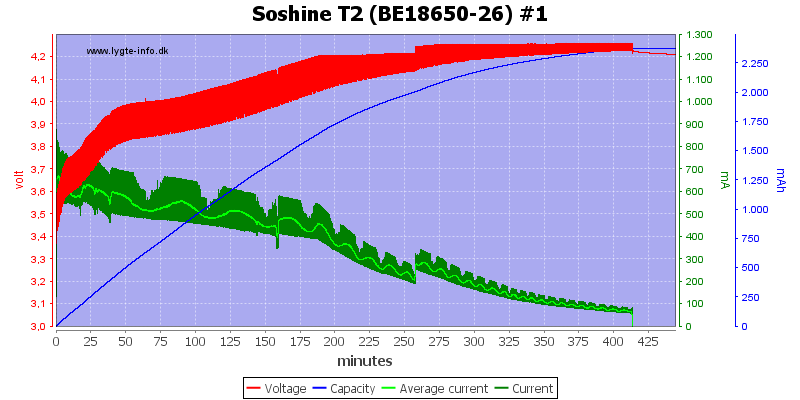
Also the older cell.
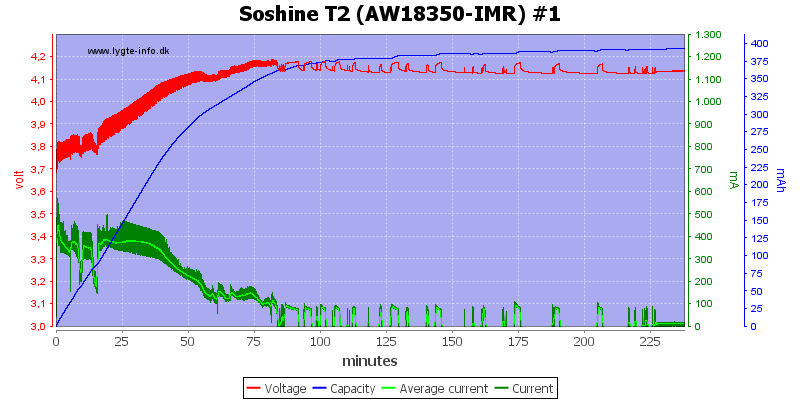
With this very old cell there is a problem, the charger restarts due to the voltage drop.
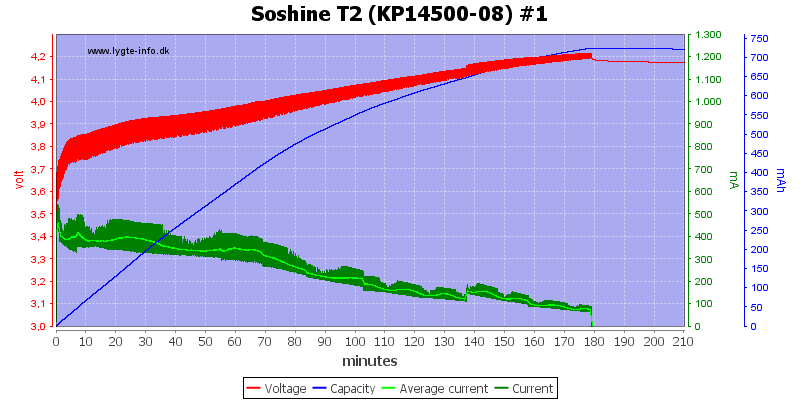
This cell looks much better.
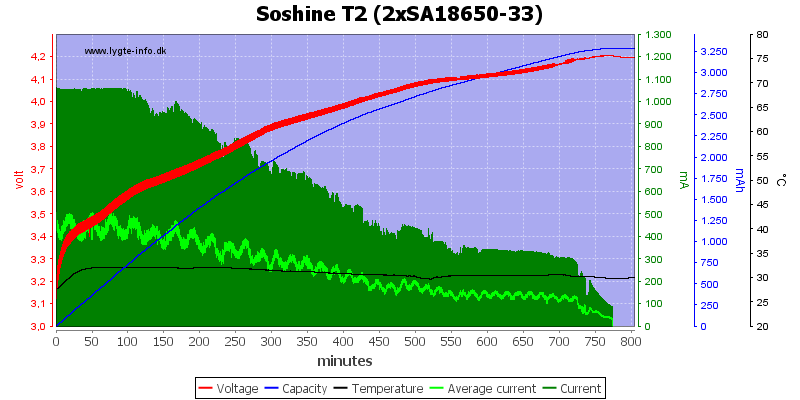
The charger speeds goes down with two batteries in the charger.
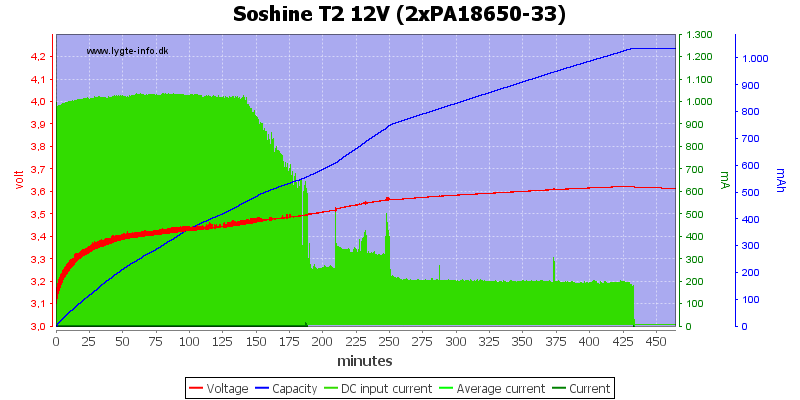
The charger uses about 1A from usb.
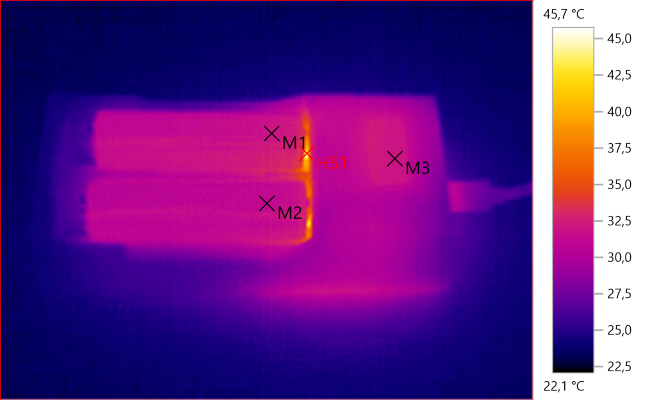
M1: 31,9°C, M2: 31,5°C, M3: 32,0°C, HS1: 45,7°C
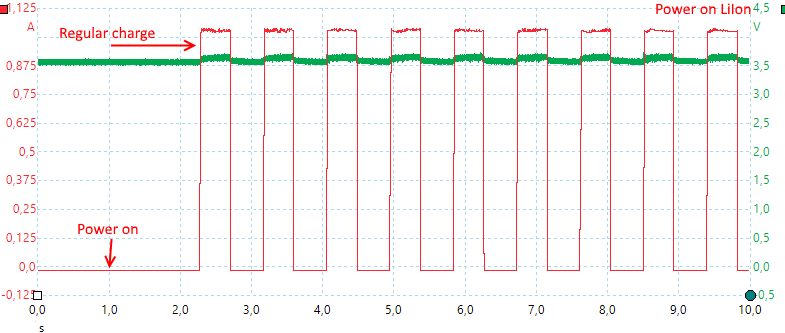
The charger starts in about 1.5 second, the initial charge is some sort of 20 second analysis phase.
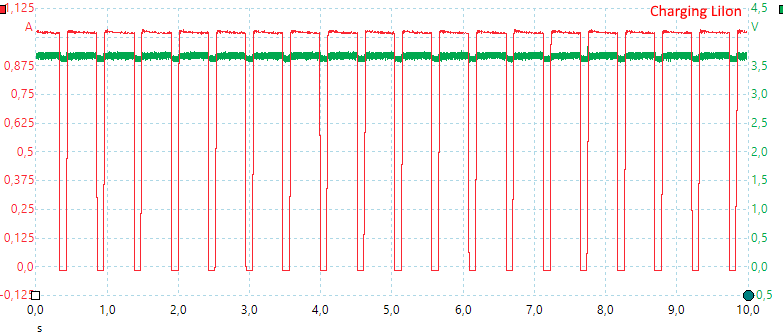
Then it decreases the pauses (At least when charging on cell).
Charging 3.6V LiFePO4
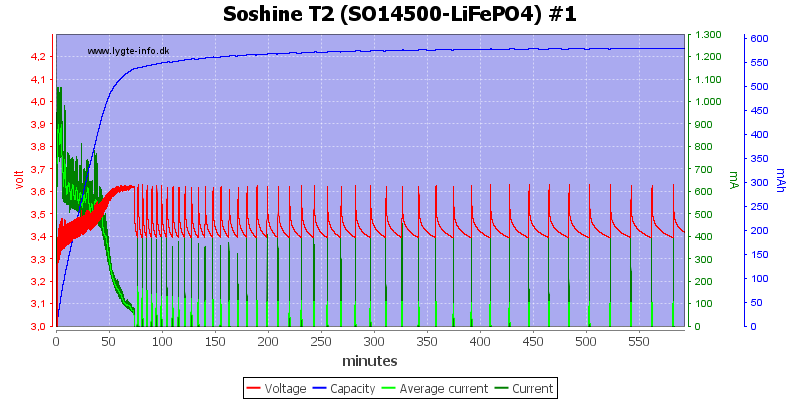
With LiFePO4 the charger has a problem with constant restart due to voltage drop.
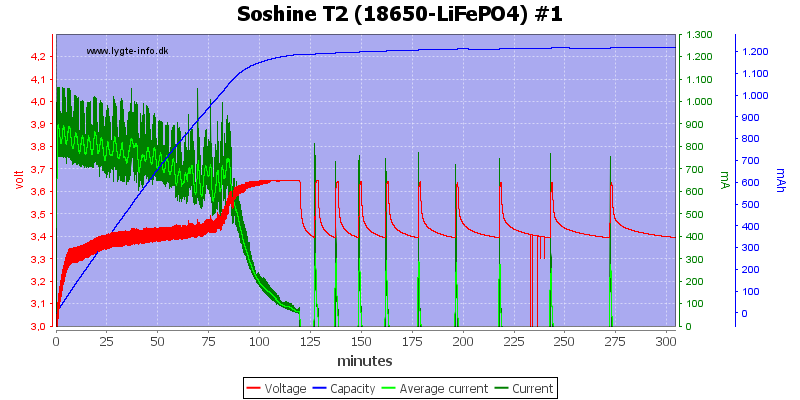
This is also the case with both the tested LiFePO4 batteries.
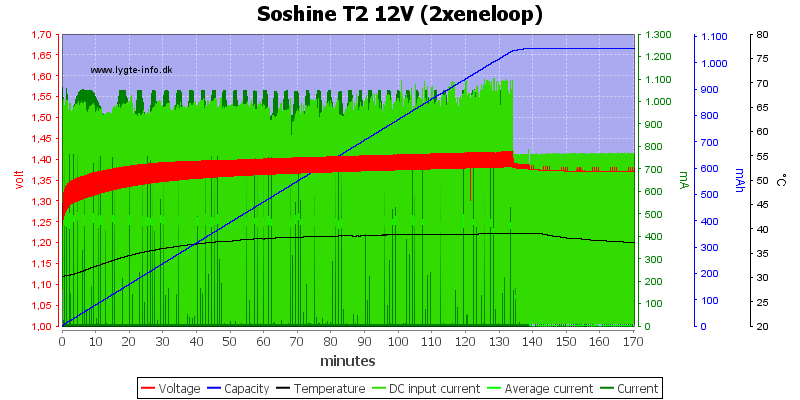
Charging NiMH
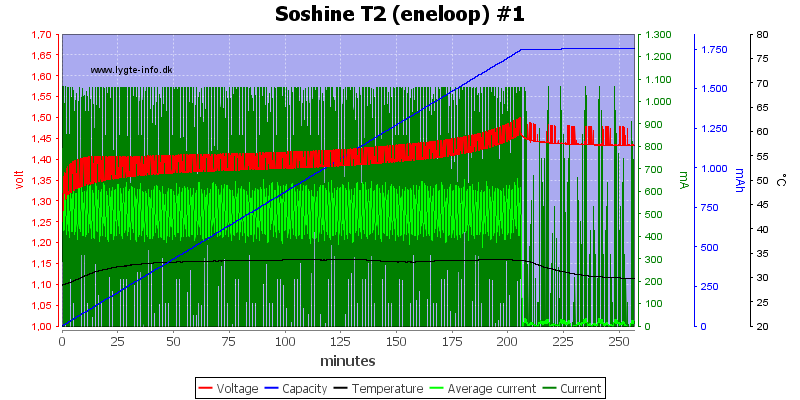
The NiMH charging terminates on voltage, but there is a low trickle charge after termination.
The cell is not filled completely during charge, the trickle charge will fill it, but it will take a long time.
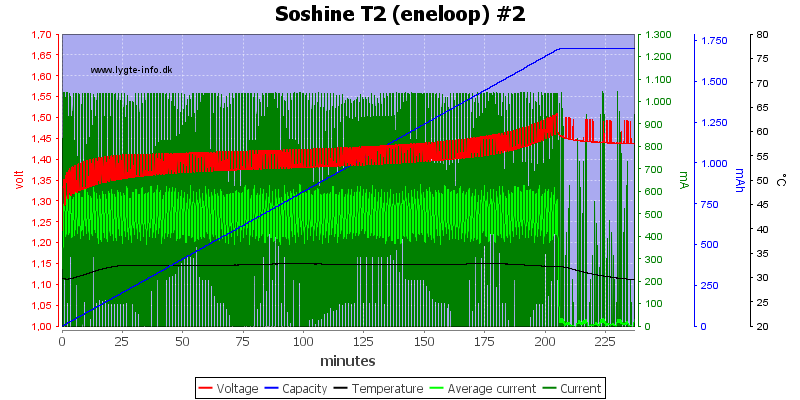
It is the same on the second channel.
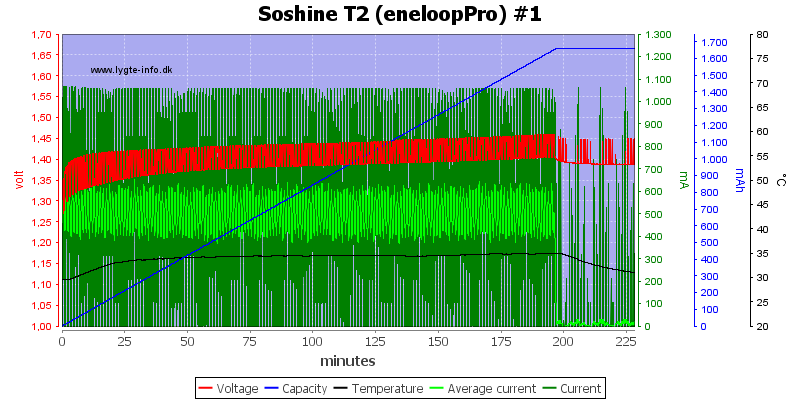
This older cell is not fully charged.
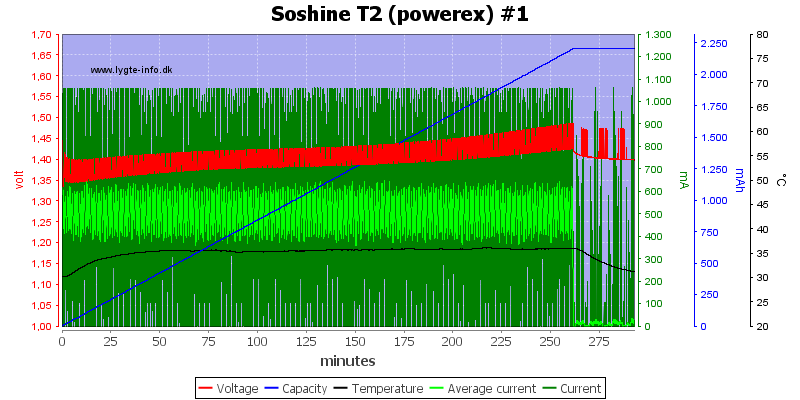
It works better on the Powerex, but there is no temperature raise at the end, i.e. the cell is not fully charged.
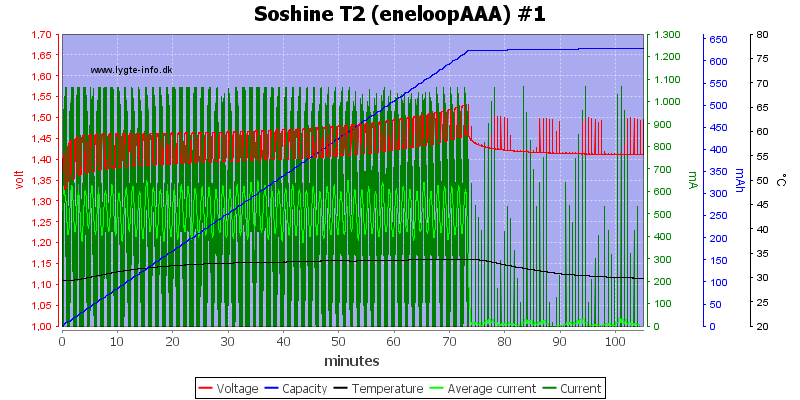
The AAA looks fine.
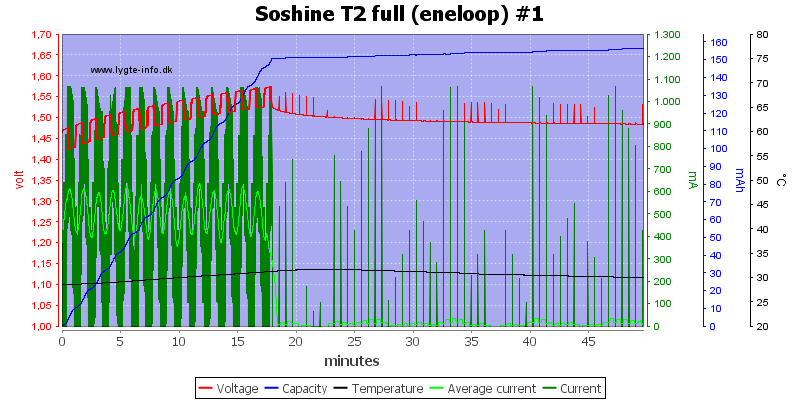
Terminating on voltage makes it fairly easy to terminate on a full cell.
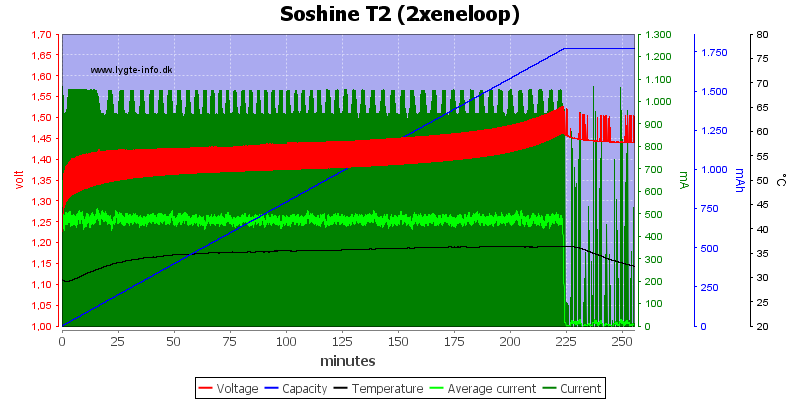
Charge speed is the same with two cell as with one.
The charger uses 1A pulses from the usb charger.
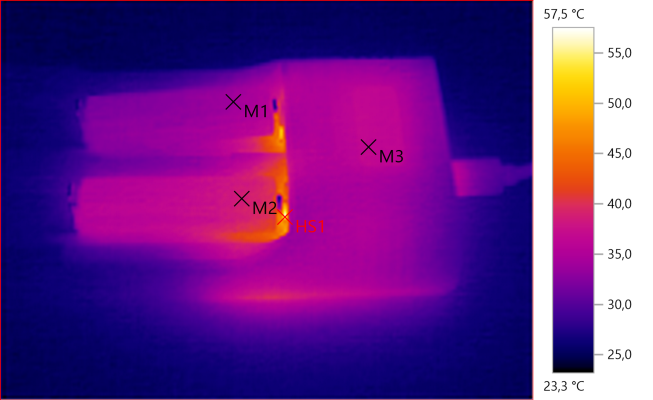
M1: 34,1°C, M2: 38,7°C, M3: 36,8°C, HS1: 57,5°C
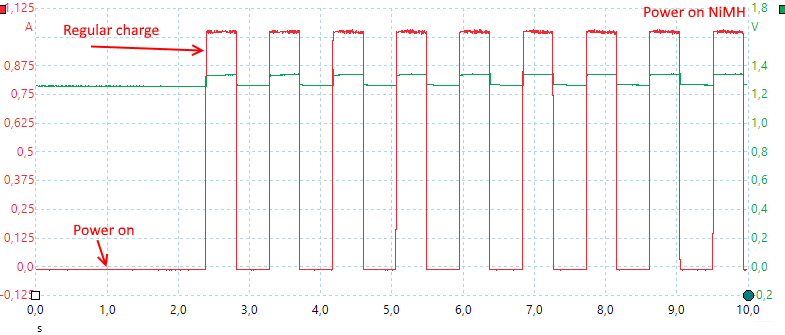
The charger needs about 1.5 second to start, with NiMH the pulsing will be use during the full charge.
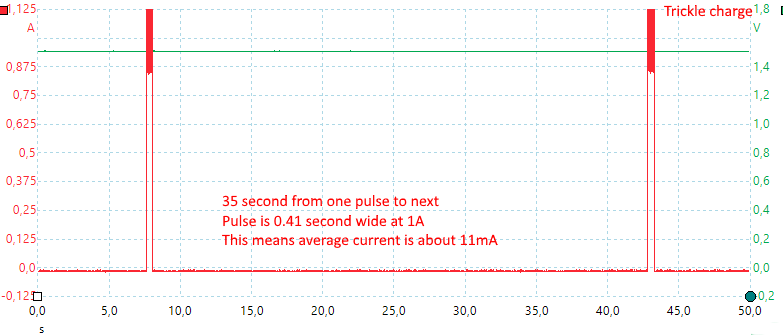
The trickle charge is done with pulses.
USB power supply
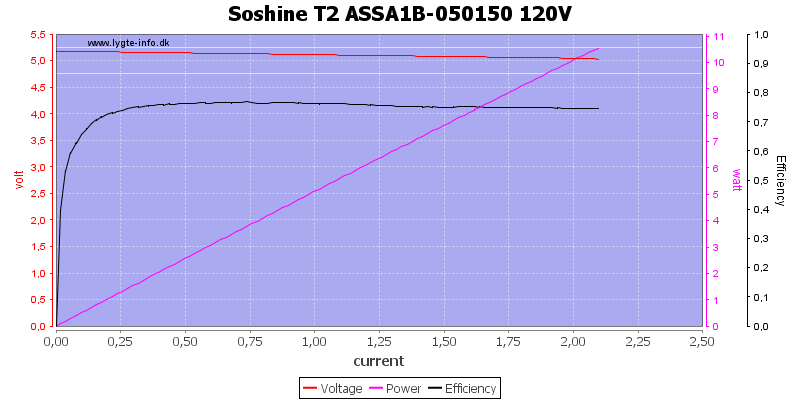
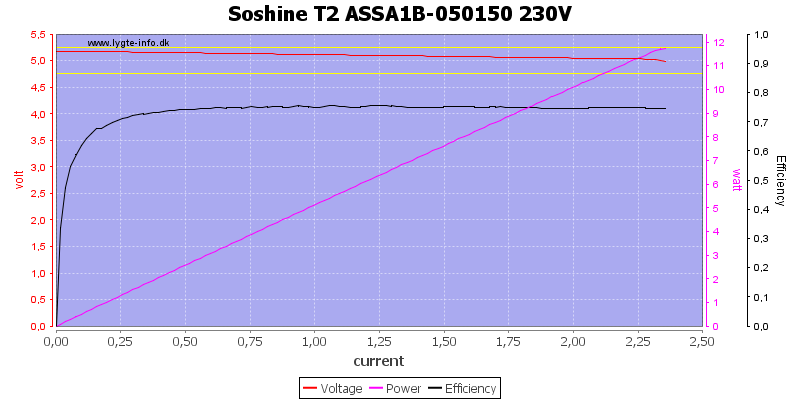
The supplied usb power supply can deliver up to 2A at least for a short time.
Testing the power supply with 2830 volt and 4242 volt between mains and low volt side, did not show any safety problems.
Conclusion
The charger curves are not looking nice, but they work. The charger is not very fast to charge the cells and the termination on LiIon/LiFePO4 is not very good.
For NiMH it uses voltage termination without top-off and with a nice low trickle charge.
I do not know why one slot died during my tests.
I will rate the charger as acceptable.
Notes
The charger was supplied by Banggood for review.
One channel on the charger died during my tests, I do not know why.
Here is an explanation on how I did the above charge curves: How do I test a charger